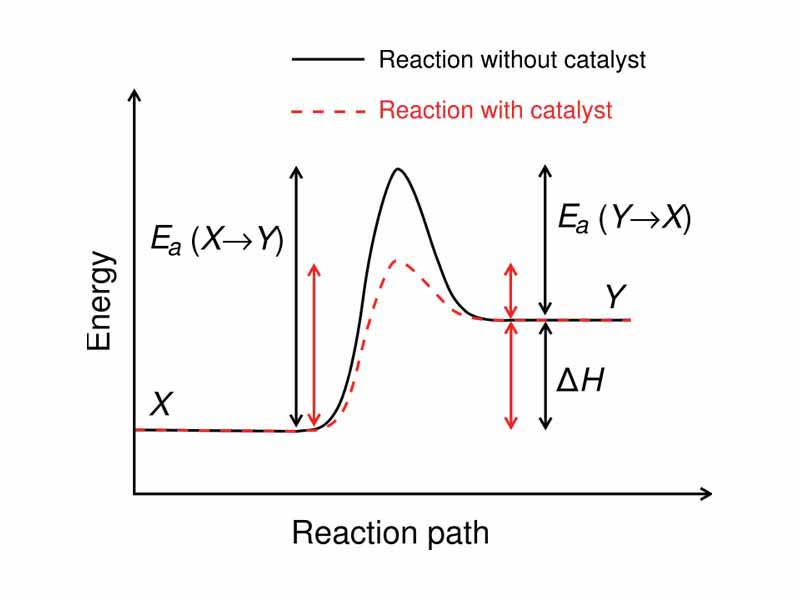
Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics . Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; example of homogenous catalysis:
from integrated-mcat.com
Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. example of homogenous catalysis: Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids;
Integrated MCAT Course
Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. example of homogenous catalysis:
From chemistnotes.com
Acid base catalysis General vs specific Chemistry Notes Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. example of homogenous catalysis: brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From wou.edu
Chapter 7 Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes Chemistry Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. example of homogenous catalysis: in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From slidetodoc.com
Chapter 23 Catalysis in Organic Reactions and in Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; example of homogenous catalysis: in acid. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From pubs.rsc.org
Dynamic parallel resolution of αferrocenyl cation initiated by Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. in this. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.researchgate.net
Hydrodeoxygenation pathway on (a) acid catalyst (b) noble metal Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. example of homogenous catalysis: a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. in acid catalysed. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.chemistrysteps.com
Ester Hydrolysis Acid and BaseCatalyzed Mechanism Chemistry Steps Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. example of homogenous catalysis: . Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From guidefixcasiranilv.z4.web.core.windows.net
How To Read Energy Diagrams Chemistry Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. in this section, we will. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The Organic Chemistry of EnzymeCatalyzed Reactions Revised Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: Catalysts lower. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.researchgate.net
Proposed mechanism of imidazole moiety formation by the acidcatalyzed Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. . Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From rumble.com
AcidBase Catalysis, Catalyst Types, Chemistry Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid,. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From br.pinterest.com
Mechanism of AcidCatalyzed Hydrolysis of An Ester with a Tertiary Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 2 from and mechanism of oxidation of some αhydroxy Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. example of homogenous catalysis: the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. . Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
Acid Catalysis of Organic Reactions Why It Works Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. example of homogenous catalysis: the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.mdpi.com
Catalysts Free FullText of Catalytic Decarboxylation of Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics example of homogenous catalysis: in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood and intracellular fluids; Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. in this section, we. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.researchgate.net
Main activation modes of chiral phosphoric acid catalysis. Download Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: example of homogenous catalysis: Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.semanticscholar.org
[PDF] Green Lewis acid catalysis in organic synthesis Semantic Scholar Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics example of homogenous catalysis: Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. Acid catalysis a common example of homogeneous catalysts are acids and bases. a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From www.researchgate.net
The methanol synthesis mechanism and for the reaction on ZnO Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in acid catalysed reactions, where c is an acid, transfer of proton to s takes place giving y as a conjugate base of c. a catalyst is a substrate that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. Catalysts. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.
From integrated-mcat.com
Integrated MCAT Course Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics in this section, we will examine the three major classes of catalysts: Catalysts lower the activation energy barrier for a. example of homogenous catalysis: brønsted acid (proton donating) and lewis acid (electron withdrawing) are the sites that lead to catalytic activity in solid. the most effective catalyst of all is the enzyme catalase, present in blood. Acid Catalyst Chemical Kinetics.